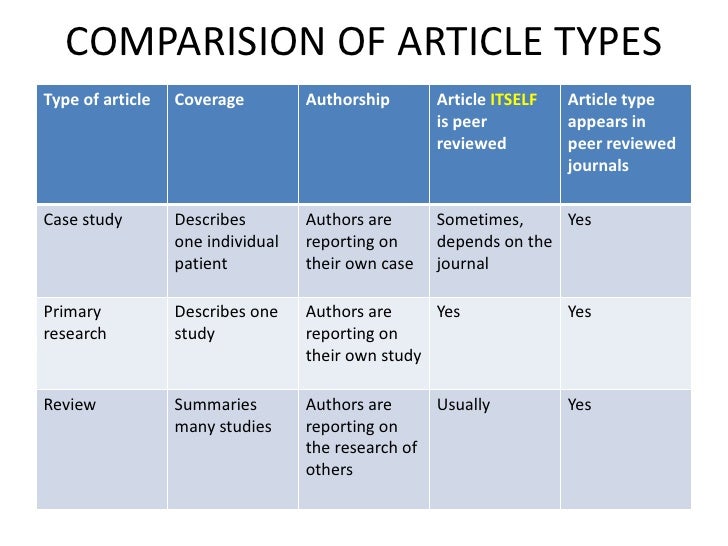
· The types of review that you conduct depends on the type of project that you are doing. The chart on the right is a useful guide to differences between systematic reviews & literature reviews. Types of Literature Reviews Below are the three main types of article reviews: 1. Journal Article Review. A journal article review is essentially a critique of an academic paper. Here, the author provides his thoughts on both strengths and weaknesses to demonstrate how it fits in with other work and what makes this publication stand out · The review article can be seen as a special case of the research article. Its purpose can vary and its format is generally less rigid than the proper research article. Furthermore, it is not uncommon to find alternative genre names used, such as review, review essay, report article, survey article and state-of-the-art survey
6 Article types that journals publish: A guide for early career researchers | Editage Insights
A systematic literature review is a method to review relevant literature in your field through a highly rigorous and 'systematic' process. The process of undertaking a systematic literature review covers not only the content found in the literature but types of review articles methods used to find the literature, what search strategies you used and how and where you searched, types of review articles.
A systematic literature review also importantly focuses on the criteria you have used to evaluate the literature found for inclusion or exclusion in the review. Like any literature review, a systematic literature review is undertaken to give you a broad understanding of your topic area, to show you what work has already been done in the subject area and what research methods and theories are being used.
The literature review will help you find your research gap and direct your research. A literature review " creates a firm foundation for advancing knowledge.
Fink p3 describes a systematic literature review as a "systematic, explicit and reproducible method for identifying, evaluating and synthesizing the existing body of completed and recorded work produced by researchers, scholars and practitioners". The purpose of your literature review will be to build a knowledge base for your research. The knowledge base will help direct your research, assist in your gap analysis, types of review articles, and give you a strong platform to direct original research to address any gaps and support your hypothesis.
A systematic literature review differs from other styles of literature review as it applies a much higher level of methodology to the process. The EPPI-Centre is a research center at the University College London. They state the key features of a systematic literature review are:.
Systematic literature reviews aim to find as much relevant research on the particular research question as possible and to use explicit methods to identify what can reliably be said on the basis of these studies.
Methods should not only be explicit but systematic with the aim of producing varied and reliable results. In this way, systematic reviews reduce the bias which can occur in other approaches to reviewing research evidence EPPI In this case, clarity means the creating of a clear structure for the review and establishing c lear methods and documentation of the searching process.
This will allow for easy navigation and interpretation of its contents and make it easier to judge what you have done and clearly demonstrate why certain research materials have been included while others have been excluded.
It is recommended that you are very clear in what you are trying to achieve with your literature review, keep the review focused, and show each step of your methodology to ensure that the readers can follow your arguments and see where you are going and why, types of review articles. For a literature review to be a valid research output, it should seek to be unbiased regarding the literature that is reviewed. When crafting a literature review you need to be very mindful to employ a range of voices to show clear reasoning behind the inclusion of particular papers and theories, types of review articles.
To avoid publication bias, types of review articles, be sure to search a wide range of resources for the materials you include in your literature review.
Auditability, a key feature of a systematic literature review, pertains to the keeping of accurate records of your systematic search types of review articles. Accurate record keeping of your search strategies will allow others to verify your results, the records will give types of review articles readers an understanding of how you came to find and choose the materials in your review types of review articles give your review an extra layer of authority.
Auditability is a crucial part of the review process, the review must be consistent and systematic throughout. Griffith University. myGriffith Staff portal Contact us. Library Library guides Systematic literature reviews for education and social sciences Introduction. Get help. Systematic literature reviews for education and social sciences A guide to conducting a systematic literature review in the Education discipline.
Introduction Different types of literature review Developing the research types of review articles Developing your search strategies Toggle Dropdown Search strategies Recording your systematic searching Systematic reading of the literature Writing your literature review Software tools Citing your sources References. Introduction What is a systematic literature review A systematic literature review is a method to review relevant literature in your field through a highly rigorous and 'systematic' process.
Definition A literature review " Purpose The purpose of your literature review will be to build a knowledge base for your research. Features A systematic literature review differs from other styles of literature review as it applies a much higher level of methodology to the process.
They state the key features of a systematic literature review are: its use of explicit and transparent methods its adherence to following a standard set of research stages its requirement that the review is accountable, replicable and up-dateable its requirement of user involvement to ensure reports are relevant and useful.
Aim Systematic literature reviews aim to find as much relevant research on the particular research question as possible and to use explicit methods to identify what can reliably be said on the basis of these studies. Validity For a literature review to be a valid research output, types of review articles, it should seek to be unbiased regarding the literature that is reviewed. Auditability Auditability, a key feature of a systematic literature review, pertains to the keeping of accurate records of your systematic search strategies.
Subjects: Education. Tags: Literature Reviewsystematic reviews, types of review articles. Except where otherwise noted, content on this site is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.
Types of Reviews
, time: 8:25Types of Article Reviews: Formats and Tips on Writing - blogger.com
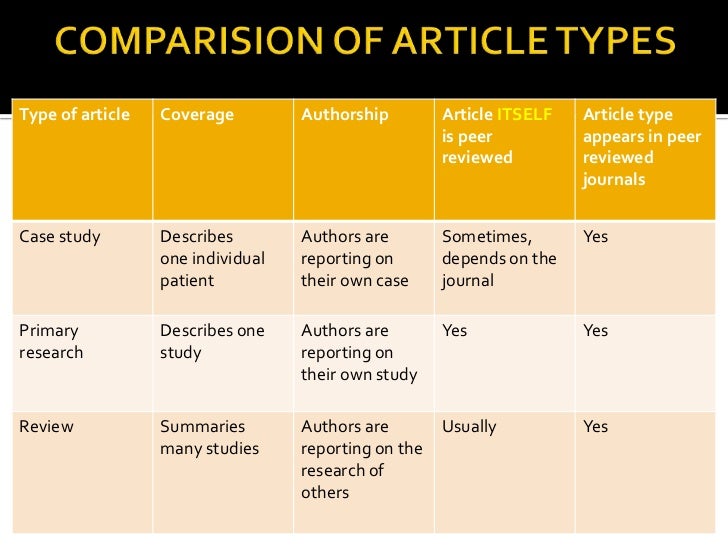
· The types of review that you conduct depends on the type of project that you are doing. The chart on the right is a useful guide to differences between systematic reviews & literature reviews. Types of Literature Reviews · The review article can be seen as a special case of the research article. Its purpose can vary and its format is generally less rigid than the proper research article. Furthermore, it is not uncommon to find alternative genre names used, such as review, review essay, report article, survey article and state-of-the-art survey Types of Reviews: Critically Appraised Topic (CATs): A critically appraised topic (or CAT) is a short summary of evidence on a topic of interest, usually focussed around a clinical question. A CAT is like a shorter and less rigorous version of a systematic review, summarising the best available research evidence on a topic
No comments:
Post a Comment